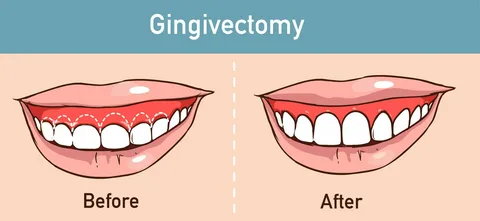
Gingivectomy: A Comprehensive Guide
A gingivectomy is a dental surgical procedure that involves the removal of a portion of the gum tissue. This treatment is often used to treat gum disease, improve the appearance of the gums, or prepare for restorative dental procedures. By removing excess gum tissue, a gingivectomy can help reduce pockets that harbor bacteria, promote better oral hygiene, and create a more aesthetically pleasing gum line.
When is Gingivectomy Needed?
A gingivectomy may be recommended for the following reasons:
Treatment of Gum Disease:
When gum disease progresses into the more severe stages (periodontitis), the gums may recede or form deep pockets around teeth. A gingivectomy can remove infected tissue and reduce these pockets to prevent further infection.Overgrown Gums (Gingival Hyperplasia):
Some patients develop overgrown gum tissue, often due to medications, poor oral hygiene, or hormonal changes. Gingivectomy can help trim and shape the gum tissue for a healthier mouth and improved appearance.Gummy Smile Correction:
A gingivectomy can be used to reshape the gums, improving the proportion of the gums to the teeth for a more balanced smile.Preparation for Dental Restorations:
Before procedures like crowns, veneers, or bridges, a gingivectomy may be performed to ensure that there is enough healthy gum tissue and to create a better fit for restorations.
The Gingivectomy Procedure
Consultation and Planning:
Your dentist will assess your oral health and determine if a gingivectomy is the right procedure. They may take X-rays to evaluate the health of your gums and teeth.Local Anesthesia:
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, numbing the affected area to ensure you feel no pain during the surgery.Removal of Gum Tissue:
Using specialized surgical instruments, the dentist carefully removes the excess or diseased gum tissue. The procedure may be done with a scalpel, laser, or electrosurgery depending on the complexity and the dentist’s preferred method.Smoothing and Shaping:
Once the gum tissue is removed, the dentist may smooth and shape the remaining gums to ensure a proper contour and fit around the teeth.Post-Procedure Care:
After the procedure, the gums may be swollen and tender. Your dentist may provide you with instructions on oral care, pain management, and what to avoid during recovery. Stitches may be used to help the gums heal, but they are usually dissolvable.
Benefits of Gingivectomy
Improved Oral Health:
By removing infected or diseased gum tissue, gingivectomy can help reduce the risk of gum disease progression, reduce gum inflammation, and eliminate pockets that trap bacteria.Enhanced Aesthetics:
The procedure can improve the appearance of a “gummy smile” or uneven gum lines, giving the teeth a more symmetrical and natural appearance.Restores Gum Contour for Restorations:
Gingivectomy provides the proper gum structure for fitting dental crowns, bridges, or other restorative work, ensuring a better outcome for these procedures.Prevention of Further Gum Problems:
Removing infected tissue prevents the spread of gum disease, helping to protect the teeth and bones from long-term damage.
Recovery After Gingivectomy
Pain and Discomfort:
After the procedure, mild to moderate discomfort is common. Pain medication and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to alleviate any pain or swelling.Swelling and Bleeding:
Swelling and some minor bleeding can occur after the procedure, but these typically subside within a few days.Oral Hygiene:
Proper oral hygiene is essential during the recovery period. You may be advised to use a special mouth rinse and avoid brushing directly over the surgical area until it heals.Diet:
For the first few days after the surgery, you should stick to soft foods and avoid hot, spicy, or hard foods that could irritate the gums.Follow-Up Appointments:
Your dentist will likely schedule follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and to monitor the gums for any signs of infection or complications.
Risks and Considerations
Infection:
As with any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of infection after a gingivectomy. Following proper aftercare instructions can minimize this risk.Changes in Gum Line:
The removal of gum tissue can affect the appearance of your gums and teeth. In some cases, more tissue may need to be removed, or the gum line may need further shaping to achieve the desired results.Tooth Sensitivity:
Some patients experience increased tooth sensitivity after the procedure due to exposed tooth roots. This should subside over time as the gums heal.
Is Gingivectomy Right for You?
Gingivectomy is a highly effective treatment for people suffering from gum disease, overgrown gums, or an unbalanced gum-to-tooth ratio. If you are considering this procedure, it’s essential to consult with a periodontist or dentist to determine if it’s suitable for your specific needs.
Key Features about Gingivectomy
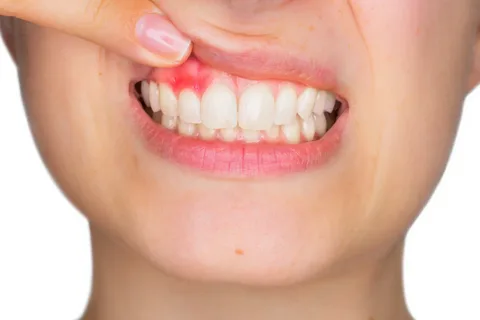
Treatment for Gum Disease

Improves Aesthetic Appearance
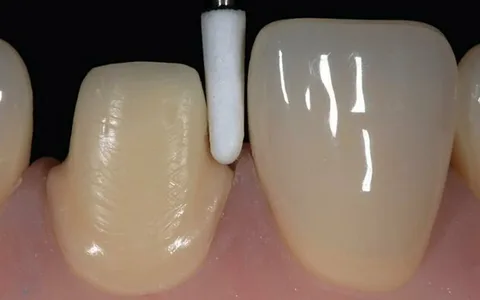
Preparation for Dental Restorations
Frequently asked questions
Here are descriptions for FAQs about Gingivectomy to provide a clear understanding:
A gingivectomy is a surgical procedure where a portion of the gum tissue is removed to treat gum disease, improve the appearance of the gums, or prepare the gums for dental restorations.
Gingivectomy is typically recommended for treating gum disease, removing excess or overgrown gum tissue, correcting a gummy smile, or preparing for dental treatments like crowns or bridges.
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, so you shouldn’t feel any pain during the surgery. Some mild discomfort or swelling may occur during the recovery period.
Recovery time varies depending on the extent of the procedure, but most patients recover within 1 to 2 weeks. It’s important to follow post-operative care instructions for optimal healing.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks, including infection, bleeding, or changes in the gum line. Following aftercare instructions helps minimize these risks.