Gum Surgery
Gum surgery, also known as periodontal surgery, is a dental procedure aimed at treating advanced gum diseases or improving the aesthetics and functionality of the gums. It addresses problems like gum recession, excessive gum tissue, or gum infections that cannot be managed through non-surgical treatments.
Gum surgery is an effective solution for advanced gum problems, offering both functional and cosmetic benefits. While it requires proper care and recovery, the long-term advantages outweigh the temporary discomfort. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining oral hygiene are essential to prevent recurrence. Always consult a dental professional to determine the best course of action for your gum health.
Why is Gum Surgery Needed?
- Treat Advanced Periodontal Disease: To remove bacteria, plaque, and tartar from beneath the gums and reduce infection.
- Repair Gum Recession: To cover exposed tooth roots and protect teeth from further damage or sensitivity.
- Correct Gummy Smiles: To remove excess gum tissue for a more balanced and aesthetic appearance.
- Prepare for Dental Procedures: Such as creating a stable foundation for dental implants.
- Prevent Tooth Loss: Stabilizes teeth by improving the health and strength of the gums and supporting structures.
Types of Gum Surgery
Gingivectomy:
- Purpose: Removes excess gum tissue caused by gum disease or a gummy smile.
- Procedure:
- The dentist trims and reshapes the gum tissue using a scalpel or laser.
- Local anesthesia is used, and the area is sutured if necessary.
- Recovery: Healing takes about 1–2 weeks.
Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery):
- Purpose: Treats deep gum pockets caused by periodontal disease.
- Procedure:
- The gums are lifted to clean plaque and tartar from deep pockets.
- The gums are then sutured back tightly to reduce pocket depth.
- Recovery: Healing occurs within 1–2 weeks; swelling and discomfort are common initially.
Gum Grafting:
- Purpose: Treats gum recession by covering exposed roots.
- Procedure:
- Tissue is taken from another part of the mouth (usually the palate) or a donor source.
- The graft is sutured to the affected area to restore gum coverage.
- Recovery: Healing can take 2–4 weeks, with dietary restrictions during recovery.
Bone Grafting and Regenerative Surgery:
- Purpose: Restores lost bone and gum tissue caused by severe gum disease.
- Procedure:
- Bone graft material is placed in areas of bone loss.
- Growth-stimulating proteins may be applied to encourage tissue regeneration.
- Recovery: Healing varies; follow-up visits are essential to monitor progress.
Crown Lengthening Surgery:
- Purpose: Removes gum and sometimes bone to expose more of the tooth structure, often for restorative or cosmetic purposes.
- Procedure:
- Excess gum tissue is removed, and the area is reshaped to create a balanced gumline.
- Recovery: Initial healing occurs in about a week, but complete recovery may take 6–8 weeks.
Preparation for Gum Surgery
- Diagnosis:
- X-rays and a thorough examination to assess gum health and identify the severity of the problem.
- Treatment Planning:
- Discussing the type of surgery, expected results, and post-operative care.
- Oral Hygiene:
- Ensuring the mouth is as clean as possible before the procedure.
Key Feature about Gum Surgery
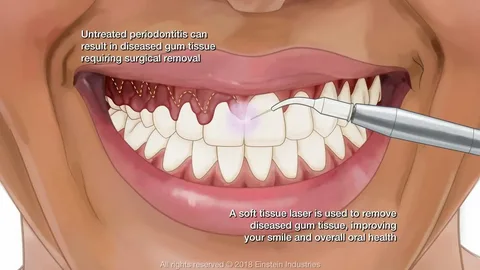
Treats Advanced Gum Disease
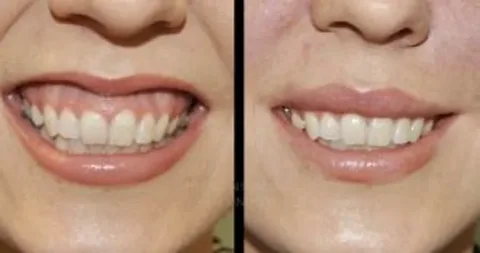
Repairs Receding Gums
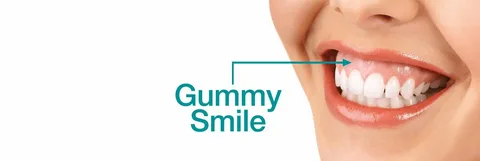
Enhances Smile Aesthetics
Frequently asked questions
Here are descriptions for FAQs about Gum Surgery to provide a clear understanding:
Gum surgery is a dental procedure to treat gum disease, repair gum recession, or improve aesthetics.
It’s needed to treat advanced gum disease, correct gum recession, improve a gummy smile, or support dental restorations.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, so you won’t feel pain during surgery. Mild discomfort afterward is manageable with pain relievers.
- Gingivectomy: Removes excess gum tissue.
- Flap Surgery: Cleans deep pockets.
- Gum Grafting: Repairs recession.
- Crown Lengthening: Exposes more of the tooth.
Your dentist may advise professional cleaning, medication, and avoiding smoking or alcohol before surgery.
